If you think you have abdominal aortic aneurysm, you are in the right place. This condition can be a life-threatening medical condition. Fortunately, there is no specific cause of abdominal aneurysm, and you can live a healthy life despite its effects. There are several signs and symptoms of this condition, including pulsing pain and a discolored or distorted abdomen.
While abdominal aortic aneurysm symptoms are often hard to detect, they should not be ignored. Patients with risk factors should be hypervigilant. Those with a family history of abdominal aortic aneurysmas are about twelve times more likely to develop one. Other risk factors include being a smoker, having high blood pressure, and having atherosclerosis. It is also important to note that men are more likely to develop abdominal aneurysms. If you suspect that you might be suffering from an aneurysm, consult your doctor immediately. Your medical team can prescribe a plan of care that can detect it and treat it as soon as possible.
There are two main types of procedures for abdominal aneurysm. Surgical repair involves replacing the affected part of the aortic arch with synthetic tubing. A number of other treatments are available that reduce the risk of an aneurysm rupture. Non-surgical treatments include lowering cholesterol levels and quitting smoking. You can undergo routine ultrasound scanning to monitor the size of the aneurysm.
After the aneurysm is diagnosed, treatment can be initiated. The aim of the surgery is to treat the underlying disease and prevent its occurrence. While medicines can lower blood pressure, they can’t shrink aneurysms once they’ve formed. For patients who already have an aneurysm, the best option is open surgery. The surgeon will make an incision in the belly and sew a graft onto the damaged aorta section. This procedure requires a hospital stay of four to ten days and can take several months to recover.
While most people with abdominal aortic aneurysm do not have any symptoms, they should be monitored by their doctor. In addition to avoiding unnecessary treatments, a person should consult a physician and have a full medical examination. In addition to the usual medications, they must also undergo ultrasound scans to assess the aortic artery’s health.
Symptoms and Treatment of Abdominal aneurysms are dependent on the severity of the condition. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. MRIs can show an aneurysm, but cannot diagnose it unless it is large. Smaller abdominal aneurysms can be treated with medication, while larger aneurysms may require surgery.
A large aortic aneurysm, also called a pseudoaneurysm, may not cause symptoms. The symptoms of abdominal aortic aneurysm are throbbing abdominal pain, tenderness in the chest, and a pulsating sensation in the abdomen. Usually, most people do not experience any of these symptoms. However, if you experience a throbbing or pulsing sensation in the abdomen, it could be a sign of a ruptured aneurysm.
Most people with abdominal aortic aneurysms will not have any symptoms. Imaging tests may show a bulge in the aorta, but they do not cause any symptoms. In most cases, a ruptured aortic aneurysm will not rupture until it reaches a large size. Acute abdominal pain is the most common symptom of an aneurysm, and if you have any type of acute pain, it will be the first symptom that a doctor will recommend.
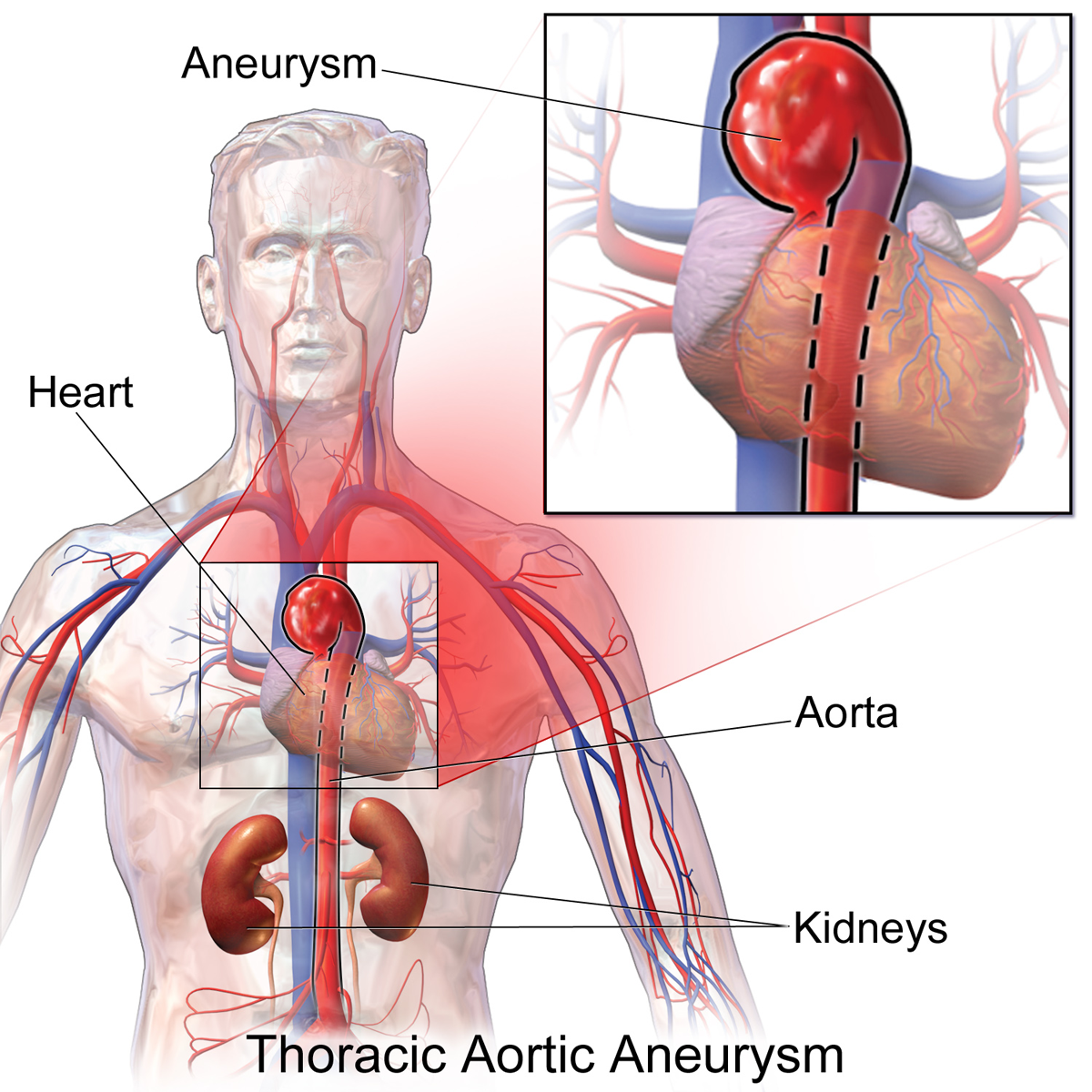
The aorta is the largest blood vessel in the human body. If an aortic aneurysm has weakened walls, the artery will expand like a balloon, forcing blood away from vital organs. This condition can lead to heart attacks and kidney damage. Thankfully, it is easy to treat with surgery. Surgical treatment is usually an option, but it may be necessary.
During diagnostics, an abdominal aortic aneurysm is often diagnosed through ultrasound. A CT scan, which uses ionizing radiation to see the aneurysm, will show whether the aneurysm is benign or malignant. If you have symptoms of the condition, your doctor will recommend a procedure. If you do have a large abdominal aortic aneurysmatic, the procedure will be more complicated than a smaller aneurysm.