Brussels, January — According to parliament news, observers say the US Greenland strategy has become one of the most influential forces reshaping Arctic politics this year. From defense planning and diplomatic signaling to economic and environmental considerations, Greenland’s strategic value has moved to the forefront of international attention. As climate change accelerates Arctic transformation and global competition intensifies, decisions taken in Washington reverberate across Europe, the North Atlantic, and the wider international system.
Greenland’s Geographic Importance in a Changing Arctic
Greenland’s position between North America and Europe gives it unparalleled strategic relevance. Sitting astride emerging Arctic air and sea corridors, the island functions as a natural gateway linking continents. This geography explains why the US Greenland strategy places such emphasis on surveillance, early warning systems, and secure transit routes.
As polar ice retreats, previously inaccessible waters are opening for seasonal navigation. These shifts shorten commercial shipping routes and alter military planning assumptions, making Greenland a pivotal node in Arctic connectivity.
Historical Roots of American Engagement
American involvement in Greenland dates back to the Second World War, when defense agreements established the foundations of a long term presence. Over decades, cooperation with Denmark and Greenlandic authorities remained relatively low profile. The contemporary US Greenland strategy builds on this history but reflects a more complex geopolitical environment.
What was once a narrow security arrangement has evolved into a multidimensional approach integrating defense, diplomacy, and economic interests.
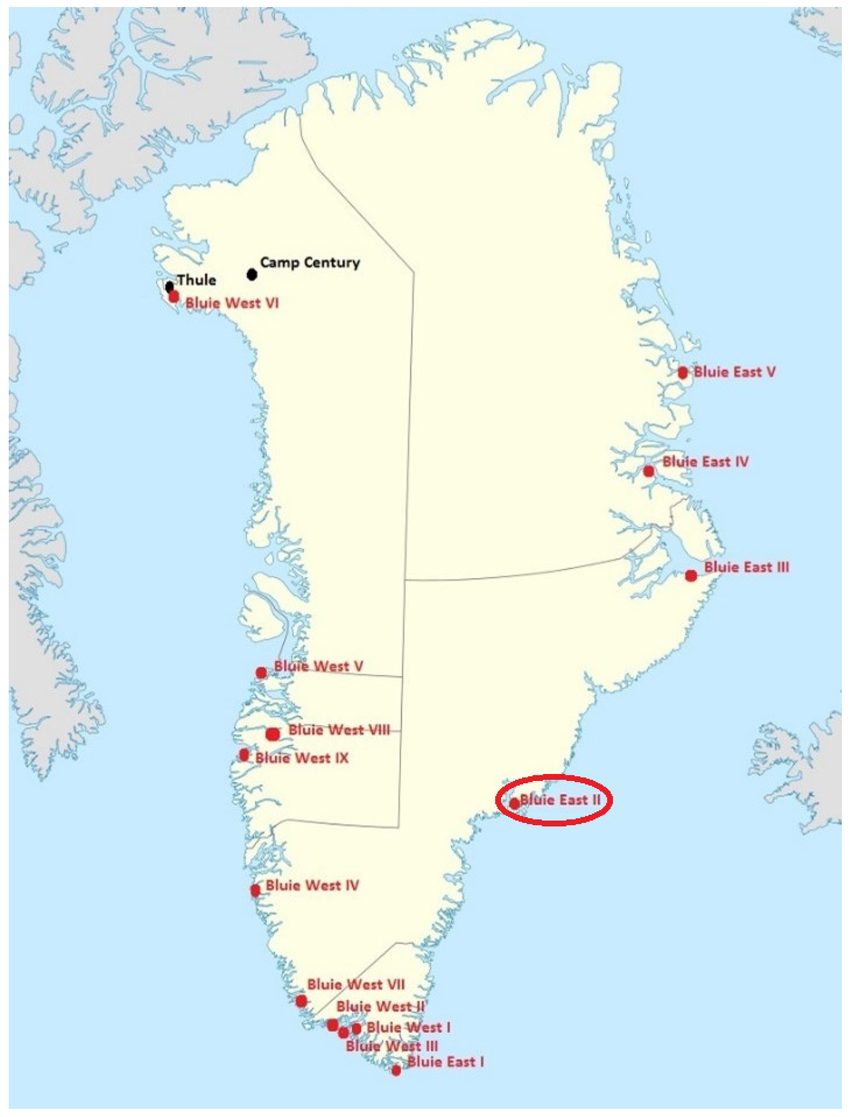
Defense Infrastructure and Strategic Deterrence
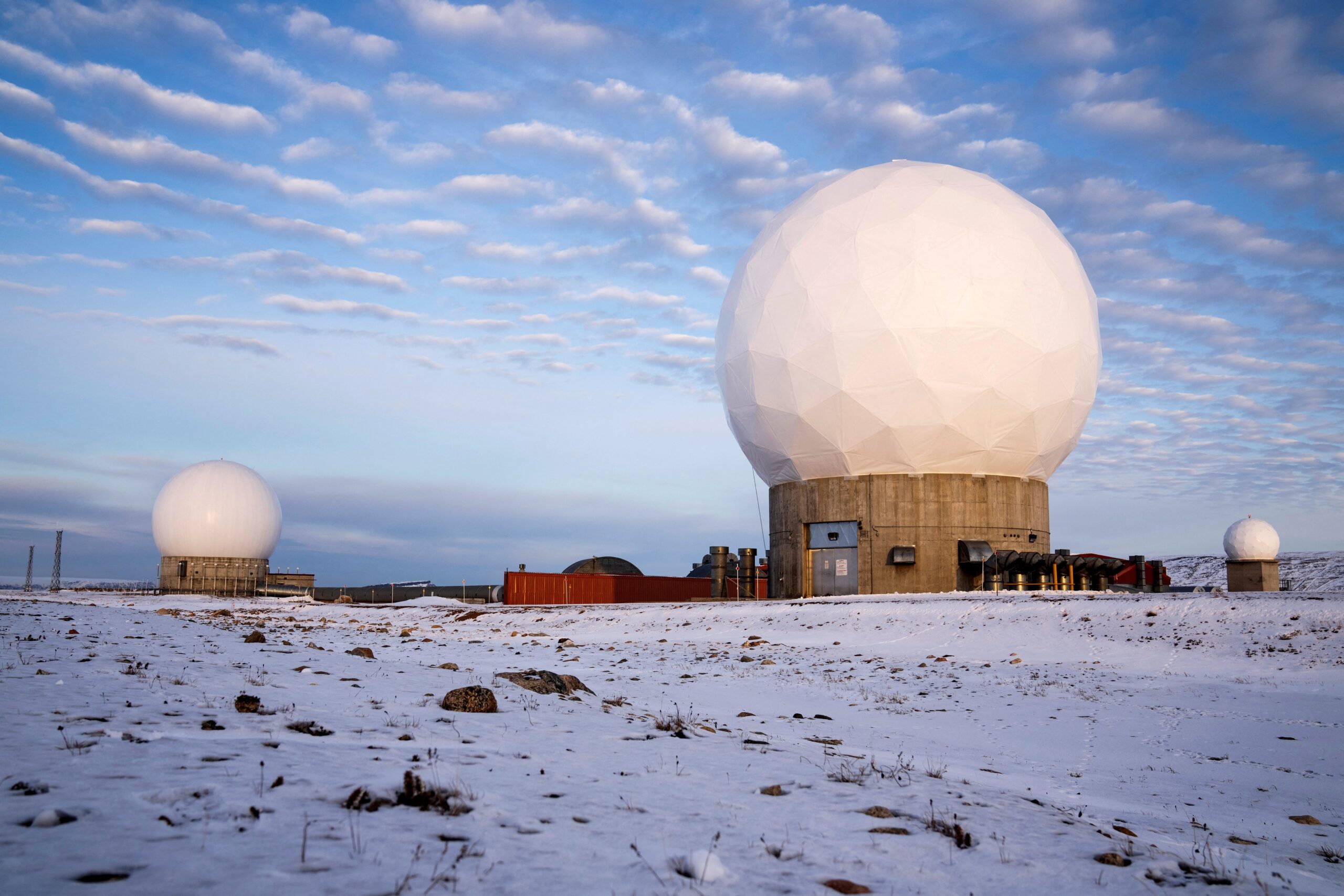
Military infrastructure remains central to Arctic planning. Radar installations and air facilities in Greenland support missile detection and aerospace monitoring across the North Atlantic. Within the US Greenland strategy, modernization of these systems is viewed as essential to maintaining credible deterrence in an era of advanced missile technology.
Defense planners argue that Arctic surveillance is no longer a peripheral concern but a core element of national and allied security.
Climate Change as a Strategic Driver
Climate change is reshaping Arctic realities faster than any other region on Earth. Melting ice alters coastlines ecosystems and accessibility. The US Greenland strategy increasingly integrates climate data into security assessments recognizing that environmental change directly affects strategic stability.
Scientific research stations environmental monitoring and disaster response planning now intersect with traditional defense objectives.
Economic Interests and Resource Considerations
Greenland holds significant deposits of minerals critical to modern technology and clean energy transitions. Rare earth elements have attracted international attention as supply chains face growing pressure. The US Greenland strategy seeks to ensure secure and transparent access to these resources while encouraging responsible development.
Economic engagement is framed as a way to support local communities while reinforcing long term partnerships built on shared interests.
Diplomatic Implications for Transatlantic Relations
Washington’s Arctic posture sends signals to allies and competitors alike. European governments view the US Greenland strategy as both a reassurance of commitment and a reminder of shifting power dynamics. Consultations with partners remain a key feature of Arctic diplomacy.
At the same time, differences in emphasis between North American and European approaches highlight the need for continued dialogue to preserve unity.
Arctic Governance and Multilateral Frameworks
Arctic governance relies on cooperation among states with overlapping interests. The US Greenland strategy interacts with existing institutions by emphasizing security while supporting dialogue and transparency. Officials stress that long term stability depends on maintaining rules based engagement.
Balancing national priorities with shared responsibilities remains one of the central challenges of Arctic politics.
Greenlandic Perspectives and Local Autonomy
Greenlandic leaders consistently emphasize the importance of autonomy cultural preservation and sustainable development. Economic opportunities generated by heightened interest must align with local priorities. The US Greenland strategy increasingly reflects this reality through consultation and partnership frameworks.
Respect for local decision making is widely seen as essential to maintaining legitimacy and trust.
Public Debate and Media Attention
Media coverage of Arctic issues has expanded significantly. Greenland now features prominently in discussions of global security climate change and resource competition. One Arctic policy specialist observed,
“Greenland has moved from the margins of geopolitics to its very center.”
Such commentary reflects a broader recognition of the island’s strategic relevance.
Implications for NATO and Collective Security
Within NATO, Arctic security is gaining prominence. The US Greenland strategy influences alliance planning by highlighting the importance of northern defense and interoperability. Joint exercises intelligence sharing and infrastructure coordination are increasingly focused on Arctic scenarios.
Alliance officials underline that cohesion and coordination remain critical to effective deterrence.
Technology and Future Military Planning
Advances in satellite systems unmanned platforms and cyber capabilities are transforming Arctic operations. The US Greenland strategy incorporates these technologies to enhance situational awareness and resilience. Investment in innovation is seen as vital to maintaining an edge in a challenging environment.
Technology also enables more efficient monitoring with reduced environmental impact.
Environmental Protection and Sustainability
Environmental protection remains a central concern. Greenland’s fragile ecosystems are vulnerable to industrial activity and climate stress. The US Greenland strategy acknowledges the need to balance strategic interests with environmental stewardship.
International cooperation on conservation research and sustainable practices is increasingly emphasized.
Global Power Competition in the High North
The Arctic is no longer insulated from global rivalry. Interest from multiple powers has intensified competition. Within this context, the US Greenland strategy represents an effort to shape outcomes through presence engagement and partnership rather than confrontation.
Analysts caution that miscalculation in the Arctic could have far reaching consequences.
Economic Development and Infrastructure Investment
Infrastructure development including ports communications and energy systems is becoming more important. The US Greenland strategy supports investment that enhances resilience and connectivity while aligning with local needs.
Improved infrastructure also strengthens emergency response capabilities in a harsh environment.
Education Research and Knowledge Exchange
Scientific research plays a vital role in Arctic understanding. Collaborative projects involving universities and research institutions contribute to climate science and environmental monitoring. The US Greenland strategy recognizes research as a soft power tool fostering cooperation and shared knowledge.
Education initiatives also help build local capacity and expertise.
Strategic Messaging and Perception Management
Perception matters in geopolitics. How actions are interpreted can influence stability. The US Greenland strategy places importance on clear communication transparency and confidence building to avoid unnecessary tension.
Strategic messaging aims to reassure partners while deterring potential challengers.
Long Term Outlook for Arctic Stability
Looking ahead Arctic stability will depend on cooperation adaptability and foresight. The US Greenland strategy will continue to evolve as environmental technological and political conditions change. Policymakers face the task of managing competition without undermining collaboration.
Sustained dialogue and institutional engagement are widely viewed as essential.
Greenland at the Crossroads of Climate Security and Power
In 2026 Greenland stands at the crossroads of climate change security and global power shifts. The US Greenland strategy illustrates how geography and environment converge with diplomacy and defense. Decisions made today will shape Arctic governance and transatlantic relations for decades to come.