Brussels, February 13, 2026 — According to Parliament News, that The Starlink competitor Europe initiative is entering a decisive stage as European policymakers and satellite operators accelerate efforts to build an independent broadband constellation. In Brussels this year, discussions have shifted from ambition to execution, with funding commitments, engineering milestones, and commercial frameworks taking center stage.
The satellite broadband race is no longer confined to a single dominant provider. Europe is positioning itself to secure technological sovereignty while ensuring that connectivity standards align with regional regulations and economic priorities. Yet success will depend not only on policy direction but on market acceptance.
Strategic Motivation Behind Europe’s Satellite Vision
The Starlink competitor Europe concept reflects broader strategic goals centered on digital independence and infrastructure resilience. Connectivity has evolved into critical infrastructure supporting defense, aviation, shipping, healthcare, and emergency services. Policymakers argue that relying exclusively on non European systems creates strategic vulnerabilities.
By investing in a European constellation, Brussels aims to secure data governance, maintain regulatory oversight, and promote homegrown innovation. The initiative aligns with long term industrial policy objectives designed to reinforce Europe’s role in the global space economy.
Still, strategic autonomy must coexist with commercial competitiveness. Buyers in the telecommunications market prioritize speed, latency, affordability, and reliability above geopolitical narratives.
Market Conditions and Competitive Dynamics
The global satellite broadband sector is expanding rapidly, driven by low Earth orbit technology capable of delivering high speed internet with reduced latency. Early entrants established global footprints through aggressive satellite deployment and consumer marketing.
In this environment, Starlink competitor Europe faces the challenge of entering a competitive marketplace shaped by technological scale and brand familiarity. Achieving comparable performance benchmarks is essential for enterprise adoption.
Telecommunications operators, aviation companies, maritime fleets, and rural broadband providers assess satellite services through measurable criteria. Coverage density, installation efficiency, and customer support infrastructure influence purchasing decisions.
Europe’s aerospace heritage provides a strong technical base. However, timing and execution will determine whether the initiative can translate engineering capability into sustainable market share.
Funding Structures and Financial Sustainability
Building a satellite constellation requires substantial investment. Satellite production, launch services, spectrum licensing, and ground station development generate high capital expenditure.
The Starlink competitor Europe initiative relies on a coordinated funding framework combining public resources with private sector investment. This blended model seeks to ensure long term sustainability rather than short term symbolic achievement.
Revenue generation will depend on diversified streams, including government contracts, enterprise subscriptions, and consumer broadband packages. Pricing strategies must balance affordability with operational cost recovery.
Investors are closely watching cost management and deployment timelines. Delays or overruns could influence market perception, while disciplined financial governance may strengthen credibility.

Commercial Viability and Buyer Expectations
Commercial success hinges on meeting buyer expectations. Corporate clients require service level agreements guaranteeing uptime and bandwidth stability. Consumer households expect simple installation and predictable monthly costs.
A senior aerospace executive in Brussels noted,
“A satellite network succeeds only when customers trust its performance as much as its promise.”
This observation underscores a central reality: technological independence alone cannot secure adoption. Performance consistency and competitive pricing remain decisive factors.
Starlink competitor Europe must therefore prioritize operational reliability alongside policy alignment.
Technology Infrastructure and Innovation
Low Earth orbit satellites operate closer to Earth than traditional geostationary systems, significantly reducing signal delay. This improvement supports real time communication, cloud integration, and streaming services.
Engineers working on the European constellation are focusing on signal optimization, cybersecurity resilience, and adaptive bandwidth management. Integration with terrestrial networks is also critical to ensure seamless user experience.
Innovation cycles in aerospace technology are accelerating. Continuous upgrades in payload design, propulsion systems, and ground software will shape long term competitiveness.
By leveraging Europe’s research institutions and industrial clusters, the initiative aims to maintain technological parity with established providers.
Rural Connectivity and Economic Inclusion
Expanding digital access in underserved regions remains a core objective. Many rural communities across Europe face limited broadband infrastructure due to geographic and economic constraints.
Satellite connectivity offers an alternative where fiber deployment is impractical. Small businesses, agricultural enterprises, and remote educational institutions may benefit from enhanced internet access.
However, rural consumers often exhibit price sensitivity. Subsidy programs or public incentives may influence adoption rates. Ensuring that affordability aligns with operational sustainability presents a strategic challenge.
If successfully implemented, expanded connectivity could stimulate regional economic development and reduce digital inequality.
Regulatory Landscape and Governance
European regulatory frameworks emphasize data protection and consumer privacy. A domestically governed satellite system allows closer alignment with regional compliance standards.
Spectrum allocation, environmental considerations, and cross border coordination require careful management. Efficient regulatory processes may accelerate deployment while maintaining oversight.
Clarity in governance structures reassures investors and enterprise clients. Transparent oversight enhances credibility in a competitive market.
The regulatory environment will shape how effectively Starlink competitor Europe scales across member states.

Investor Outlook and Market Response
Financial markets respond to milestone announcements, launch success, and subscription growth indicators. Aerospace manufacturers and telecommunications firms may experience valuation shifts linked to project progress.
The investment community evaluates long term revenue visibility and cost discipline. Strong execution could attract global partnerships and cross border collaborations.
Market analysts note that diversified provider ecosystems often stimulate innovation and improve service standards. Competition may ultimately benefit consumers through expanded options.
Starlink competitor Europe represents both opportunity and calculated risk within Europe’s evolving digital economy.
Global Strategic Implications
Satellite broadband is increasingly viewed as a pillar of national infrastructure. Governments worldwide recognize connectivity as essential for economic competitiveness and security resilience.
By advancing Starlink competitor Europe, Brussels signals its commitment to maintaining influence within the global space sector. Diversified satellite networks may reduce systemic vulnerabilities and encourage healthy market dynamics.
International partnerships could emerge as the constellation expands. Cooperation with allied nations may enhance coverage and technological exchange.
Strategic positioning in space communications carries long term geopolitical significance.
Historic Comparison
Technological disruption within Europe’s space and telecommunications sectors is not unprecedented. During earlier transitions from analog to digital broadcasting and from terrestrial to mobile broadband, market volatility accompanied innovation.
In each case, initial skepticism gave way to mainstream adoption as infrastructure matured. Companies that invested early in modernization ultimately secured competitive advantage.
The emergence of satellite broadband echoes those prior cycles. New entrants must navigate skepticism, funding hurdles, and technical refinement before achieving scale.
History suggests that innovation initially unsettles markets but eventually establishes new norms. Whether Starlink competitor Europe follows that trajectory depends on disciplined execution and sustained demand.
Long Term Structural Outlook for Starlink Competitor Europe
The Starlink competitor Europe initiative represents far more than a symbolic response to global satellite broadband expansion. It reflects a long term strategic commitment to technological sovereignty and a more assertive role in global digital infrastructure development.
For Starlink competitor Europe to achieve sustainable success, three structural pillars must remain balanced: performance excellence, financial durability, and regulatory clarity. High speed connectivity alone will not secure market leadership. The constellation must consistently deliver measurable reliability while operating within a financially responsible framework that reassures investors and enterprise clients.
As deployment progresses, transparency will play a decisive role. Clear communication regarding satellite launches, coverage expansion, latency benchmarks, and pricing structures will influence buyer confidence. Demonstrating tangible progress strengthens the credibility of Starlink competitor Europe in a market where trust and technical proof matter more than political intention.
Long term viability also depends on adaptability. Satellite technology evolves rapidly, and customer expectations shift alongside innovation. The ability of Starlink competitor Europe to integrate upgrades, improve network efficiency, and respond to competitive pressures will ultimately determine whether the project achieves enduring relevance.
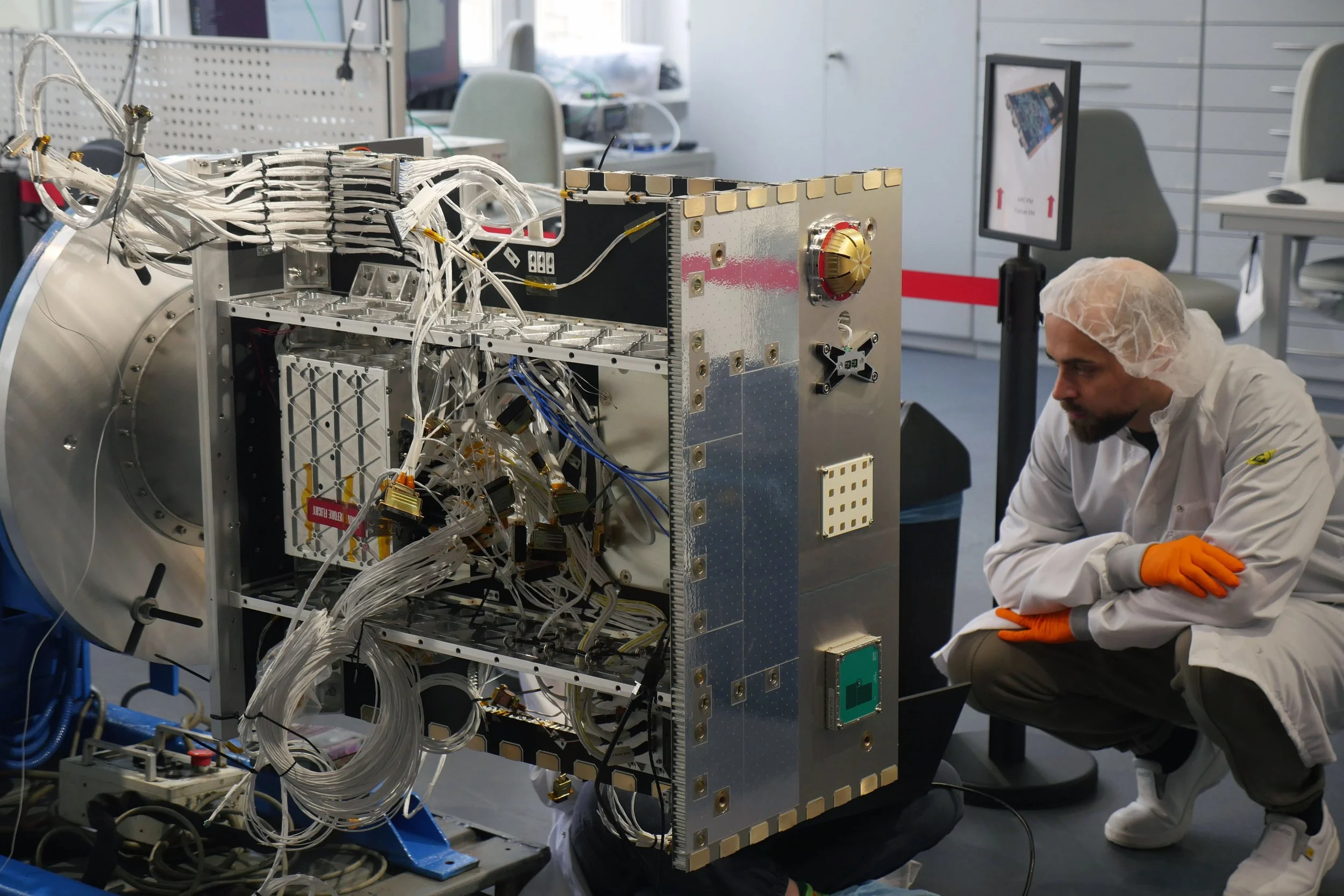
A New Digital Orbit for Europe
In 2026, Brussels stands at a pivotal crossroads where connectivity is directly linked to economic competitiveness and strategic resilience. Digital infrastructure now functions as a foundational asset comparable to energy or transportation networks.
Within this context, Starlink competitor Europe symbolizes both ambition and responsibility. It represents Europe’s determination to shape its own technological destiny while ensuring that connectivity standards align with regional priorities. However, ambition must translate into operational precision.
Achieving scale and reliability requires coordinated collaboration among governments, aerospace manufacturers, telecommunications operators, regulators, and financial stakeholders. Execution discipline will define the initiative’s credibility.
If strategic planning aligns with technical performance, Starlink competitor Europe may secure a durable position within the global satellite broadband ecosystem. Conversely, if expectations outpace delivery, competitive market forces will quickly recalibrate demand.
The coming years will reveal whether this effort becomes a defining milestone in European digital independence or remains a bold yet transitional chapter in the continent’s evolving infrastructure strategy.

