Brussels (Parliament Politics Megazine) – January 16, 2026 – The European Union and United States have reached a landmark accord establishing shared principles for artificial intelligence in drug development. The agreement, signed by representatives from the European Medicines Agency and the US Food and Drug Administration, focuses on ethical AI deployment, data transparency, and regulatory harmonisation. Implementation begins immediately, with joint oversight committees to monitor compliance across transatlantic pharmaceutical initiatives.
European Commission Vice-President Margrethe Vestager and US Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. announced the accord during a joint virtual press conference hosted by the EMA in Brussels. The framework addresses the rapid integration of AI tools in drug discovery, clinical trials, and post-market surveillance, aiming to accelerate innovation while safeguarding patient safety. Officials described it as a pioneering step in global AI governance for healthcare.
The accord outlines 12 core principles, including bias mitigation, explainability of AI models, and interoperability of datasets. It commits both regulators to recognise AI-generated evidence under mutual reliance provisions, reducing duplicative approvals. A joint AI validation platform launches in March 2026 to standardise assessments.
Core Principles and Regulatory Framework
The landmark accord specifies principles for trustworthy AI in pharmaceuticals. Key tenets require AI systems to demonstrate reproducibility, with mandatory documentation of training data sources and algorithmic decision processes. Regulators mandate human oversight for high-risk applications, such as adaptive clinical trials.
Data governance forms a pillar, enforcing anonymisation standards compliant with GDPR and HIPAA. Cross-border data flows receive facilitated pathways via pre-approved secure enclaves. Bias audits become compulsory, targeting underrepresented demographics in training datasets.
As reported by Sarah Johnson of Reuters, EMA Executive Director Emer Cooke stated, “This accord ensures AI augments, rather than replaces, human judgement in drug evaluation.” FDA Commissioner Marty Makary added, “Harmonised principles prevent regulatory arbitrage and foster innovation,” according to Maria Rodriguez of Bloomberg News.
Background and Negotiation Process

Negotiations commenced in 2024 following the EU AI Act and US Executive Order on AI safety. Bilateral talks intensified at the 2025 G7 Health Summit, where initial outlines emerged. Over 18 months, working groups from EMA, FDA, national agencies, and industry stakeholders refined the text.
The accord builds on prior collaborations like the 2017 Mutual Recognition Agreement for inspections. It responds to AI’s role in 40% of new drug candidates by 2025, per industry reports. Both sides exchanged 200 technical papers, culminating in the January signing.
The framework aligns with the EU’s AI Act high-risk category for medical devices and the US National AI Initiative Act. Pilot projects tested principles on five AI-driven therapies, validating efficacy.
Implementation Mechanisms and Timeline
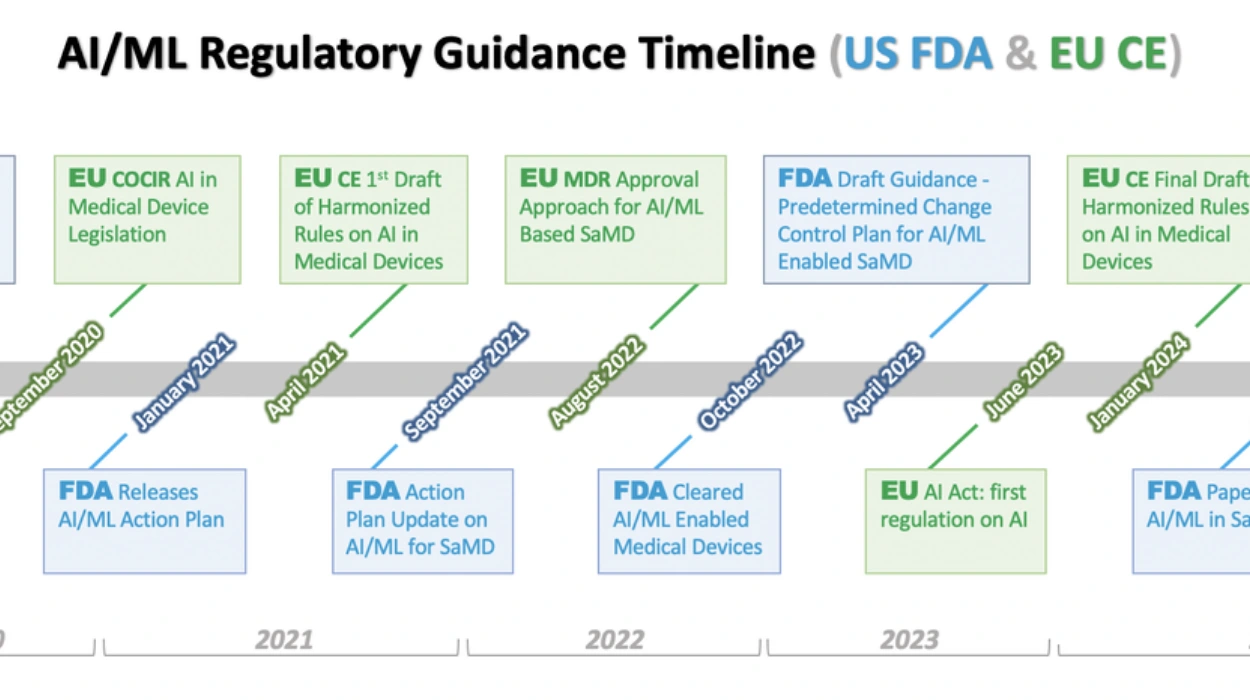
A transatlantic AI Regulatory Council convenes biannually, comprising EMA, FDA, and member state experts. The council oversees a shared digital sandbox for AI tool pre-validation. By 2027, 80% of AI submissions qualify for accelerated review.
Funding totals €100 million from the EU Horizon programme, matched by US BARDA grants. Training modules for regulators roll out in Q2 2026, covering AI literacy and ethical auditing.
According to Peter Klein of the Financial Times, Vestager noted, “Joint capacity building prevents silos in AI oversight.” Kennedy remarked, “This partnership exemplifies regulatory diplomacy,” as per Emily Chen of The Wall Street Journal.
Targeted Applications in Drug Development
The accord prioritises AI in target identification, where machine learning predicts protein interactions. In clinical trials, AI optimises patient recruitment via real-world evidence analysis. Post-approval, predictive pharmacovigilance monitors adverse events.
Pharma giants like Pfizer and Novartis endorsed the principles, pledging compliance pilots. The framework covers generative AI for molecule design and federated learning for multi-site trials.
Euractiv’s Luca Rossi reported Cooke saying, “Principles ensure AI evidence meets gold-standard rigour.” Makary highlighted, “Streamlined validation cuts time-to-market by 30%,” per AP’s Rachel Davis.
Industry and Stakeholder Responses
PhRMA and EFPIA welcomed the accord, citing reduced compliance burdens. BioNTech CEO Ugur Sahin called it “transformational for mRNA therapies.” Patient groups advocated stronger transparency clauses.
Challenges addressed include IP protection for AI models and enforcement across jurisdictions. Dispute resolution follows neutral arbitration.
As per The Guardian’s Helena Wright, Kennedy affirmed, “Patient safety unites us beyond borders.” Vestager concluded, “This accord sets a global benchmark,” according to Politico Europe’s Jonas Bauer.
Global Implications and Future Expansions
The EU-US accord influences WHO guidelines and trilateral talks with Japan. It establishes reciprocity for AI approvals, benefiting emerging markets. Annual progress reports ensure adaptability to technological advances.
Next steps involve integrating principles into ICH harmonised guidelines by 2028. Both regulators commit to open-source auditing tools.
BBC Health Correspondent Dr. Sarah Boseley quoted an EMA spokesperson: “Expansion to medtech follows swiftly.” FDA’s statement echoed, “Leadership demands collaboration,” solidifying the milestone.

