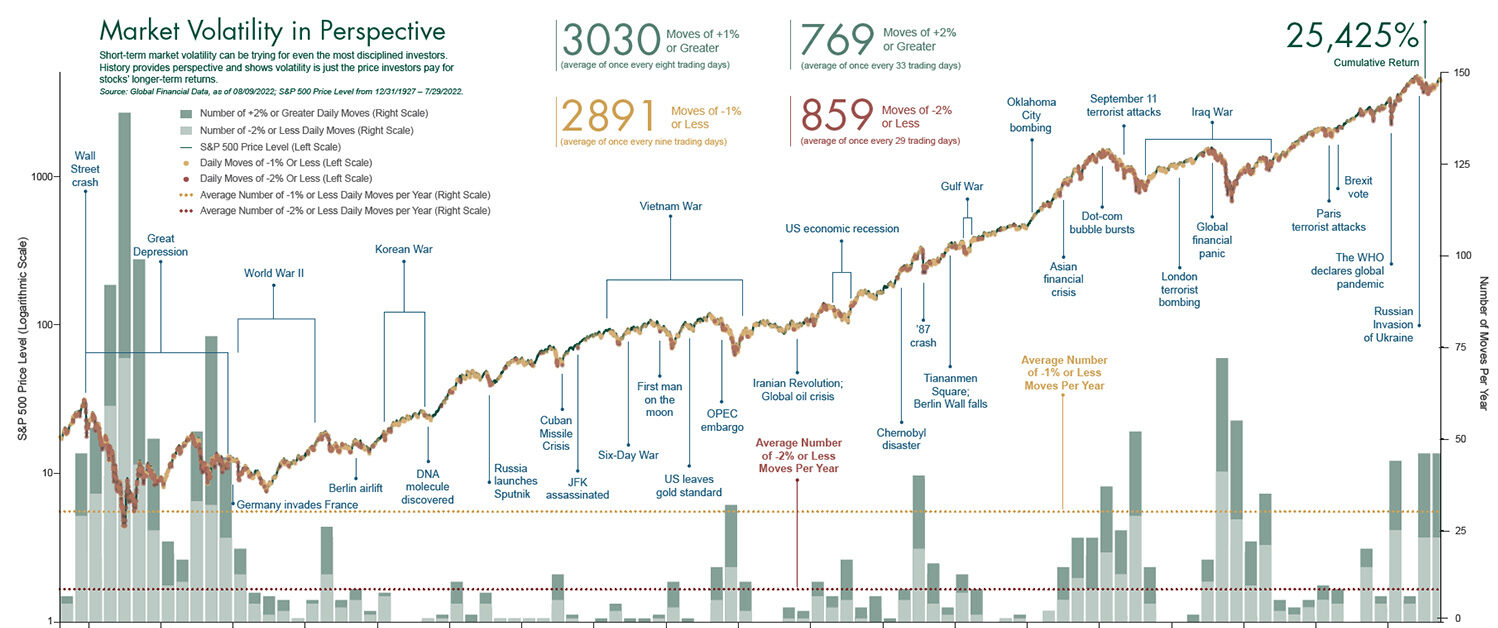
New York, January 2026 — According to parliament news., financial centers around the world opened the year under intense pressure as global markets volatility surged across equities currencies commodities and bonds. Investors navigating early 2026 are confronting a complex mix of geopolitical tension economic uncertainty and fragile trade conditions that have made sudden price swings the new normal. Analysts say the market mood reflects caution rather than panic but acknowledge that confidence has weakened across multiple asset classes.
The synchronized nature of recent moves highlights how interconnected modern financial systems have become.
Geopolitical Risk Returns as a Market Driver
Geopolitical developments once again dominate investor thinking. War rhetoric regional conflicts and diplomatic breakdowns have revived fears of supply chain disruption and energy instability. Even without direct conflict escalation the possibility alone is enough to influence trading behavior. The persistence of global markets volatility demonstrates how markets increasingly respond to perceived risk rather than confirmed outcomes.
Strategists note that uncertainty now carries a measurable financial cost.
Equity Markets Experience Sharp and Uneven Swings
Stock markets across major economies have shown wide daily fluctuations. Technology and manufacturing stocks have been particularly sensitive to trade related headlines while defensive sectors have attracted cautious capital. These divergent trends reflect selective risk pricing rather than uniform pessimism. The pattern of global markets volatility suggests investors are repositioning rather than exiting markets entirely.
Algorithmic trading has further amplified short term movements.
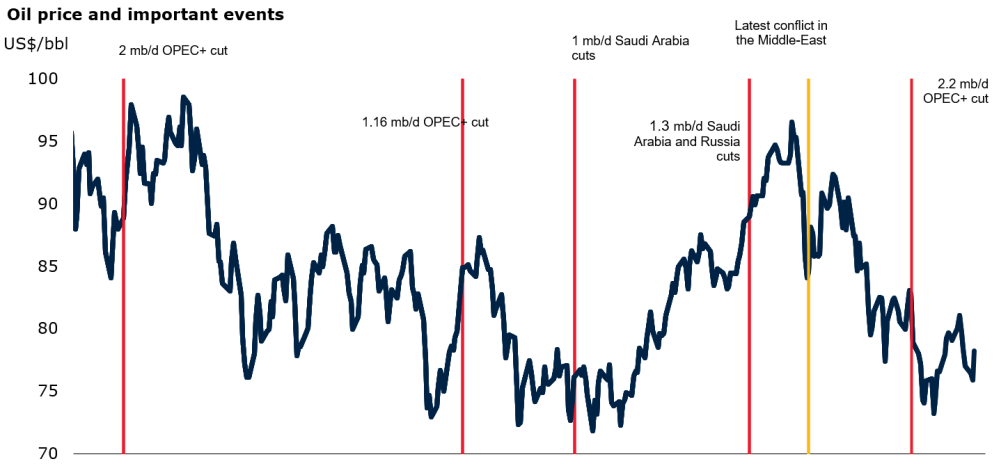
Oil Prices Amplify Market Sensitivity
Energy markets sit at the center of investor anxiety. Oil prices have reacted sharply to geopolitical developments and shipping risk concerns. While supply fundamentals remain stable expectations drive price behavior. The influence of energy costs on inflation ensures that oil remains a key transmission channel for global markets volatility across the wider economy.
Higher prices quickly translate into broader cost pressures.
Currency Markets Reflect Flight to Safety
Foreign exchange markets have mirrored global caution. Safe haven currencies strengthened while risk sensitive currencies weakened. Emerging market currencies faced added pressure as investors reduced exposure. This realignment highlights how global markets volatility reshapes capital flows in real time.
Currency instability can complicate debt servicing and trade planning.
Bond Markets Signal Uncertain Growth Outlook
Government bond yields have fluctuated as investors reassess growth and inflation trajectories. Increased demand for safe assets points to cautious expectations. Yield curve movements indicate that global markets volatility is influencing assumptions about central bank policy direction.
Fixed income markets remain a key indicator of sentiment.
Trade Routes and Supply Chains Under Scrutiny
Global trade remains vulnerable to disruption. Concentrated shipping lanes and just in time logistics leave little margin for error. Companies are revisiting sourcing strategies and inventory levels. The reemergence of global markets volatility has revived debate over supply chain resilience and diversification.
These adjustments often come with higher operating costs.
Corporate Earnings Outlook Grows Cautious
Corporate guidance has turned more conservative. Executives cite fluctuating input costs uncertain demand and geopolitical noise as constraints on forecasting. The environment of global markets volatility complicates capital expenditure and expansion plans.
Investors increasingly reward transparency and risk awareness.
Central Banks Navigate a Delicate Balance
Monetary policymakers face complex trade offs. Containing inflation without stifling growth requires precise calibration. The persistence of global markets volatility has reinforced a cautious data driven approach among central banks.
Clear communication has become essential to avoid unintended market reactions.
Emerging Economies Feel Disproportionate Impact
Developing economies face heightened vulnerability. Capital outflows currency depreciation and rising borrowing costs strain fiscal stability. For these countries global markets volatility can quickly translate into domestic economic stress.
International financial institutions monitor conditions closely.
Investor Behavior Shifts Toward Risk Management
Portfolio strategies now emphasize diversification and downside protection. Gold cash equivalents and defensive assets have gained attention. This response to global markets volatility reflects lessons from previous crises where liquidity proved critical.
Risk management now rivals return generation as a priority.
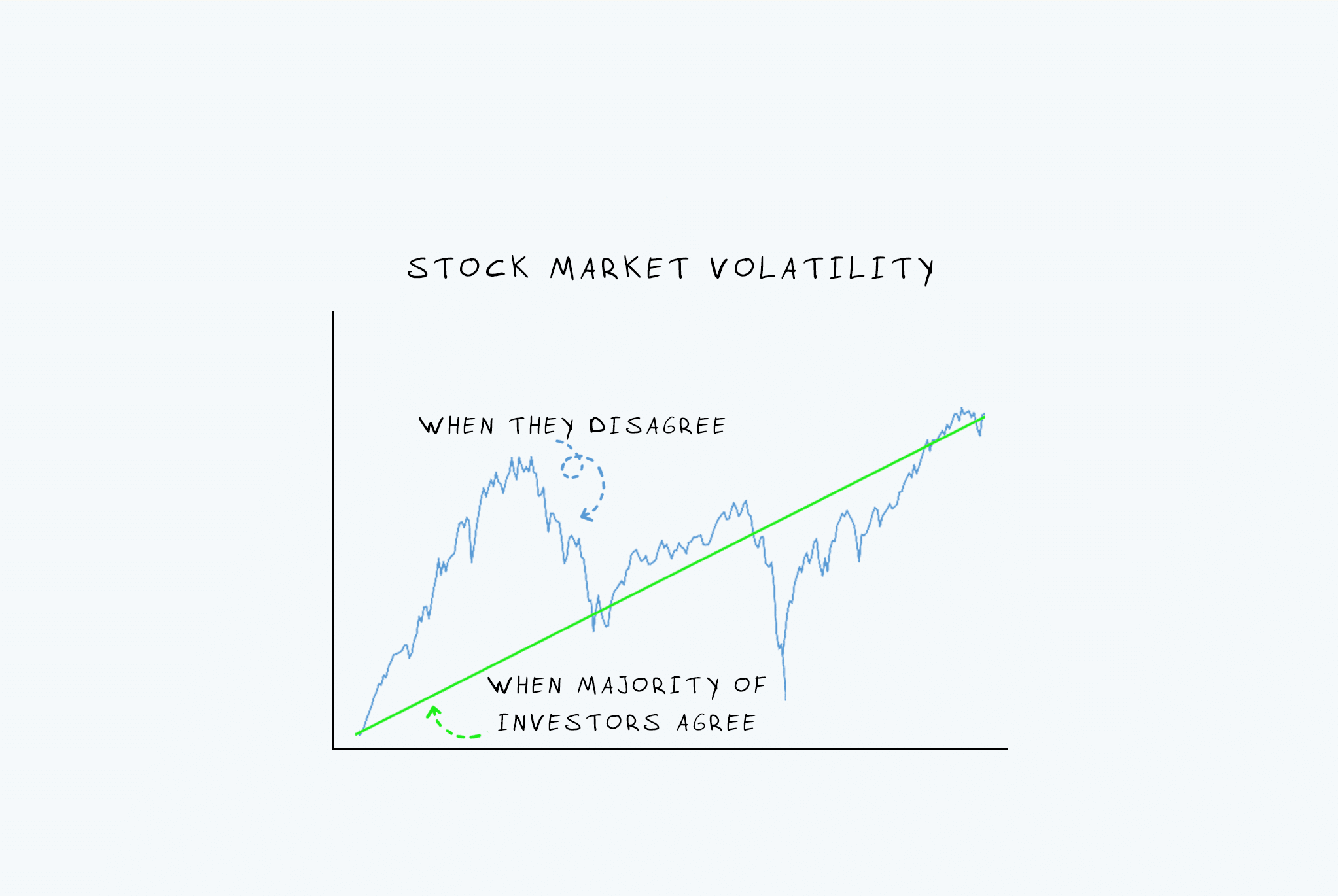
Expert View on Market Psychology
One senior market strategist observed,
“What we are seeing is not fear of collapse but fear of surprise because too many unresolved risks are overlapping at once.”
This assessment captures the psychological dimension behind recent volatility.
Technology Accelerates Market Reactions
High frequency trading and automated systems react instantly to news and data. While they enhance liquidity they can magnify price swings. In an era of global markets volatility technology acts as both stabilizer and amplifier.
Regulators continue to study structural effects.
Media Influence and Sentiment Cycles
Continuous news coverage and social media amplify emotional responses. Investor sentiment can shift rapidly as narratives evolve. This feedback loop intensifies global markets volatility beyond what fundamentals alone would justify.
Reliable information becomes a stabilizing asset.
Regional Differences in Market Resilience
Not all markets respond equally. Economies with strong fiscal positions diversified trade and credible policy frameworks show greater resilience. Others remain more exposed to external shocks. These contrasts reveal how global markets volatility exposes structural strengths and weaknesses.
Policy credibility plays a decisive role.
International Coordination and Financial Stability
Global financial institutions emphasize coordination to prevent systemic stress. Shared frameworks and communication aim to stabilize expectations. Their role grows more prominent as global markets volatility tests existing safeguards.
Confidence in institutions helps anchor markets.
Long Term Implications for Global Finance
If volatility persists investors may demand higher risk premiums raising the cost of capital. This could slow investment and growth. The endurance of global markets volatility may therefore influence economic trajectories beyond 2026.
Structural adaptation could become unavoidable.
A Defining Test for Market Resilience
As the year progresses markets face a test of adaptability. The ability to absorb shocks without cascading failure will shape confidence. The persistence of global markets volatility underscores the importance of preparedness flexibility and cooperation.
This period may redefine risk assessment norms.
Volatility Becomes a Structural Feature
The current market environment reflects a world grappling with overlapping challenges. From geopolitics and energy to trade and monetary policy the sources of instability are interconnected. As global markets volatility continues to shape behavior caution diversification and resilience have become essential strategies. Until clearer signals emerge markets are likely to remain sensitive navigating an era where uncertainty itself is the dominant force.